CAN’T STOP COUGHING? PUT AN END TO YOUR CHILD'S DISCOMFORT WITH 4 NATURAL WAYS APPROVED BY OUR IN-HOUSE NUTRITIONIST
A child's persistent cough can be a real worry for parents. Not only does it disrupt their sleep and schoolwork, but it can also make playtime less fun. As parents, it's stressful trying to figure out what’s causing your child to cough and how to make it stop.
What is Childhood Coughing?
Did you know that coughs are one of the most common reasons parents take their kids to see a doctor? While a cough can sound pretty scary, it's usually not a sign of anything serious. In fact, coughing is a healthy reflex that helps protect your child’s airways. Still, it's important to know when a cough is just a cough and when it's time to check in with a doctor.
Not All Coughs Are Equally The Same
Coughs can be different, and each type can mean something else. Here's a quick rundown of the types1,2:
Based on Duration:
Acute Cough
Duration: Lasts less than 3 weeks
Subacute Cough
Duration: Lasts between 3 and 8 weeks
Chronic Cough
Duration: Lasts longer than 8 weeks
Based on Characteristics:
Wet Cough
Also known as a productive cough as it produces mucus or phlegm. It sounds chesty and involves mucus moving in the airways. A chronic wet cough should be checked out by a doctor.
Dry Cough
Doesn’t produce mucus or phlegm and often feels like a tickle in the throat. If a dry cough lasts more than 3 weeks, it’s a good idea to consult a doctor.
Top 5 Alarming Causes of Childhood Coughing1,3
While coughing in children can manifest in various forms with specific causes, several common factors are often at the root of these different types. Here’s top 5 alarming causes of coughing in children that every parent should be aware of:
Viral Infections
The most common cause of coughs in children. Common colds and influenza are frequent culprits, often causing both wet and dry coughs as the body works to clear the virus from the airways.
Asthma
This chronic condition leads to inflammation and narrowing of the airways, resulting in a persistent dry cough, wheezing, and shortness of breath especially at night or during physical activity.
Allergies
Reactions to pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or mold can cause a dry, persistent cough due to airway inflammation and irritation.
Runny Nose Drip
Excess mucus from the nose dripping down the throat can lead to a wet cough as the body tries to clear the mucus from the airways.
Environmental Irritants
Exposure to smoke, pollution, and other environmental irritants can trigger a dry cough as the body attempts to clear the airways of these substances, and may be accompanied by eye irritation or a sore throat.
4 Best Natural Strategies to Help Stop Your Child's Never-Ending Cough4,5,6,7,8
While medical treatment is important, here are some natural ways to help your child stop coughing:
Encourage Physical Activity
Activities like running, jumping, and playing sports may strengthen your child's lungs and enhance respiratory health, thus reducing the risk of persistent coughing.
Maintain a clean air environment
A crucial factor in promoting healthy lungs is ensuring that children are exposed to clean air and smoke-free environments. By doing so, parents can help minimize respiratory irritants that trigger coughing.
Practice Good Hygiene
Encourage regular handwashing with soap and water, especially after playing outside or before meals. This simple habit helps prevent illnesses that often lead to persistent coughing.
Promote a Healthy Diet
A diet plentiful in fruits and veggies will give them the best chance at getting a variety of nutrients they need for complete health. Certain nutrients, such as vitamin C, antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids have been linked to improved lung function.
Science-Backed Foods and Herbs to Soothe Your Child’s Cough9, 10, 11,12,13
Scientific research into certain foods that offer health benefits beyond basic nutrition has revealed some may help soothe coughing in children. Here are some notable discoveries:

-
Honey
Research shows that honey can be effective in reducing coughing, particularly at night. It has natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, which help soothe the throat and reduce irritation.

-
Pears
Recognized for their soothing properties, particularly in traditional medicine. Also rich in antioxidants like vitamin C and flavonoids, which can help reduce inflammation and damage to lung tissues.

-
Ginger
Ginger has been studied for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Research suggests that ginger can help reduce inflammation in the airways and alleviate cough symptoms.

-
Red Balloon Flower Root
Has been used in traditional medicine, particularly in East Asian practices for respiratory issues. Studies have shown that the root of red balloon flower has significant expectorant and anti-inflammatory properties, beneficial in treating coughs and respiratory issues.

-
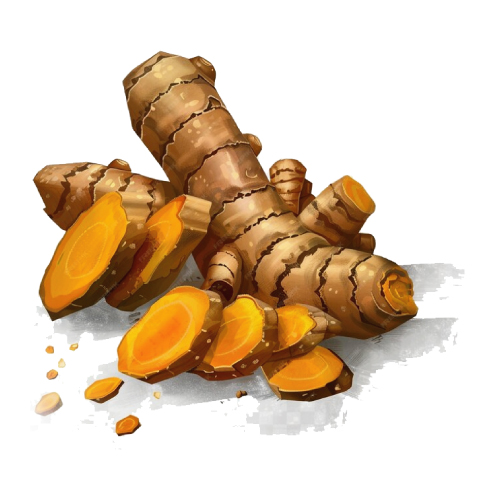
Turmeric
Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Studies suggest it can help reduce inflammation and improve overall respiratory health.
What About DDODDOMAM Red Balloon Flower & Pear Jelly?

Discover the Korean secrets to LUNG-gevity with DDODDOMAM Red Balloon Flower & Pear Jelly! Comes with the perfect combination of ingredient and function, our jelly sticks are a convenient and tasty way to promote clear airways to your child.

Our DDODDOMAM Red Balloon Flower & Pear Jelly not only unveils the legendary duo of red balloon flower root and pears but also boasts the added goodness of other natural ingredients such as honey, ginger, jujubes and many more, carefully selected to provide comprehensive respiratory nourishment for your child.

Interested to know more about this Red Balloon Flower & Pear Jelly? Learn more here. It's a delightful way to support your child’s respiratory system!
References
-
Merck & Co., Inc. (n.d.). Cough in children. MSD Manuals. https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/children-s-health-issues/symptoms-in-infants-and-children/cough-in-children#Causes_v1663385
-
Nurofen. (n.d.). Types of coughs in babies and children. Nurofen. https://www.nurofen.co.uk/children/articles/types-of-coughs-in-babies-and-children/
-
WebMD. (n.d.). Coughs and causes. WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/first-aid/coughs
-
Your lungs and exercise. (2016). Breathe (Sheffield, England), 12(1), 97–100. https://doi.org/10.1183/20734735.ELF121
-
American Lung Association. (n.d.). Secondhand smoke. Retrieved June 7, 2024, from: https://www.lung.org/quit-smoking/smoking-facts/health-effects/secondhand-smoke
-
Rabie, T., & Curtis, V. (2006). Handwashing and risk of respiratory infections: a quantitative systematic review. Tropical medicine & international health : TM & IH, 11(3), 258–267. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3156.2006.01568.x
-
Romieu I. (2005). Nutrition and lung health. The international journal of tuberculosis and lung disease : the official journal of the International Union against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, 9(4), 362–374.
-
National Institutes of Health. (2022, December 15). Omega-3 fatty acids appear promising for maintaining lung health. Retrieved from https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/omega-3-fatty-acids-appear-promising-maintaining-lung-health
-
Paul, I. M., Beiler, J. S., King, T. S., Vallati, J., & Duda, L. (2007). Effect of honey, dextromethorphan, and no treatment on nocturnal cough and sleep quality for coughing children and their parents. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 161(12), 1140-1146.
-
Townsend, E. A., Siviski, M. E., Zhang, Y., Xu, C., & Hoonjan, B. (2013). Effects of ginger and its components on airway smooth muscle relaxation and calcium regulation. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology, 48(2), 157-163.
-
Aggarwal, B. B., & Harikumar, K. B. (2009). Potential therapeutic effects of curcumin, the anti-inflammatory agent, against neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, pulmonary, metabolic, autoimmune, and neoplastic diseases. International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 41(1), 40-59.
-
Kim, S. J., Kim, M. C., Um, J. Y., & Hong, S. H. (2012). The beneficial effect of Platycodon grandiflorum on airway inflammation and related events in a murine model of asthma. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 144(2), 379-386.
-
Reiland, H. B., & Slavin, J. (2015). Systematic Review of Pears and Health. Nutrition Today, 50(6), 301-305. https://doi.org/10.1097/NT.0000000000000112